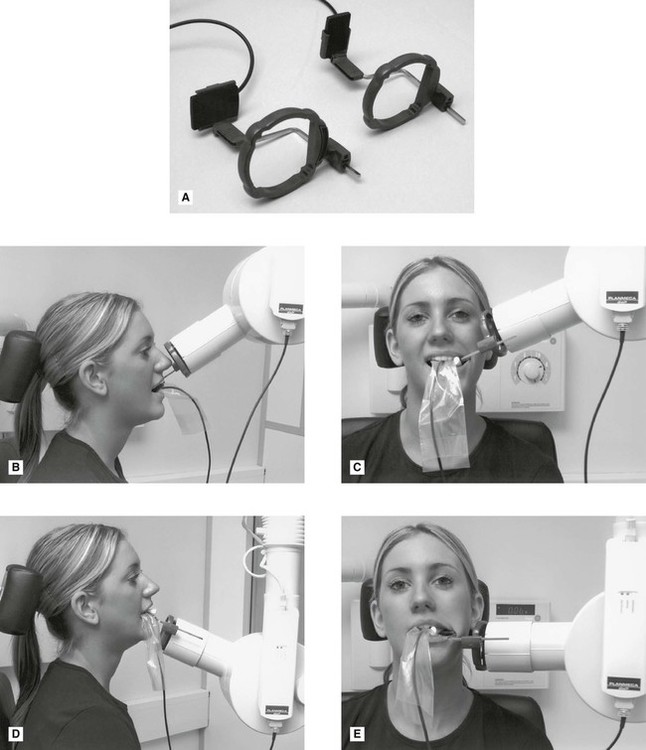
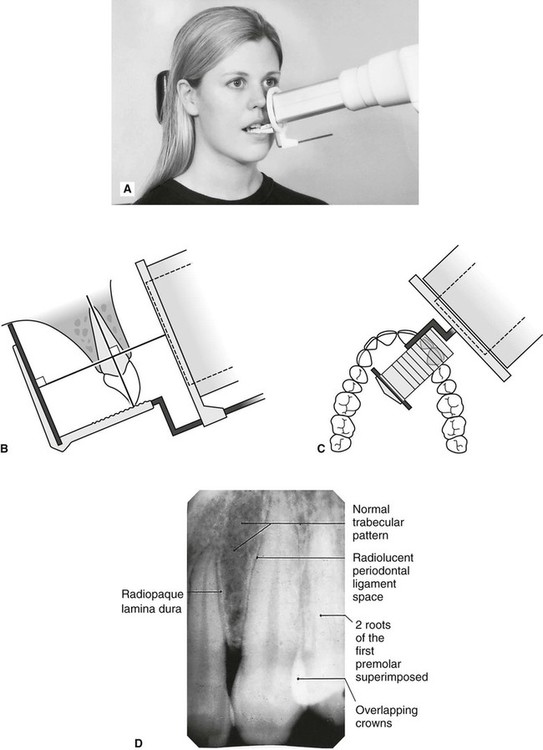
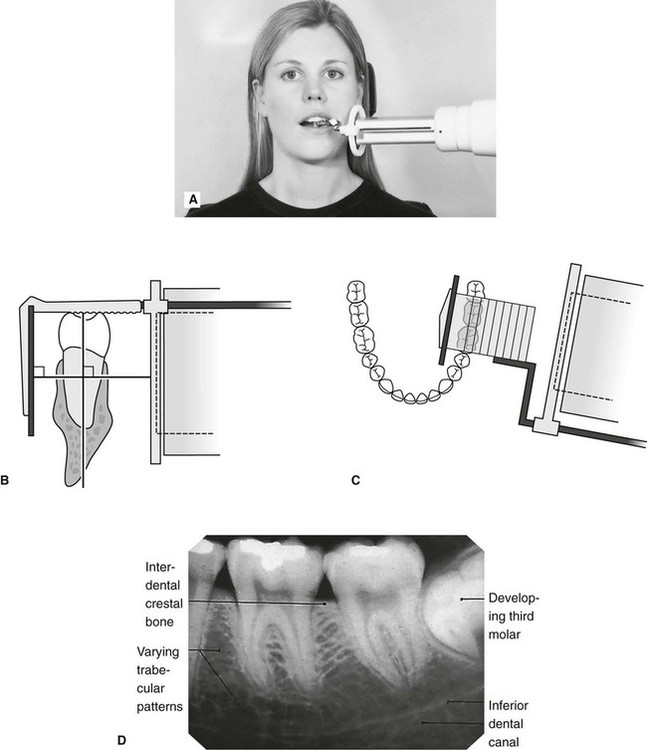
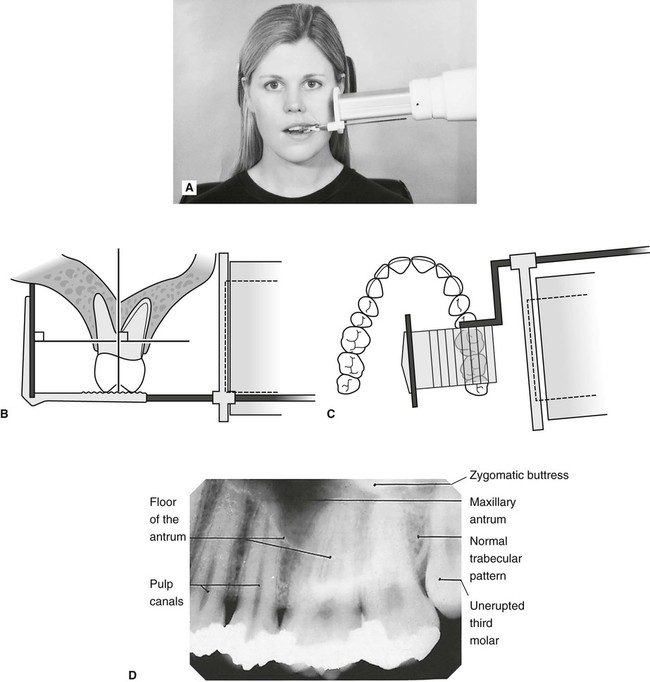
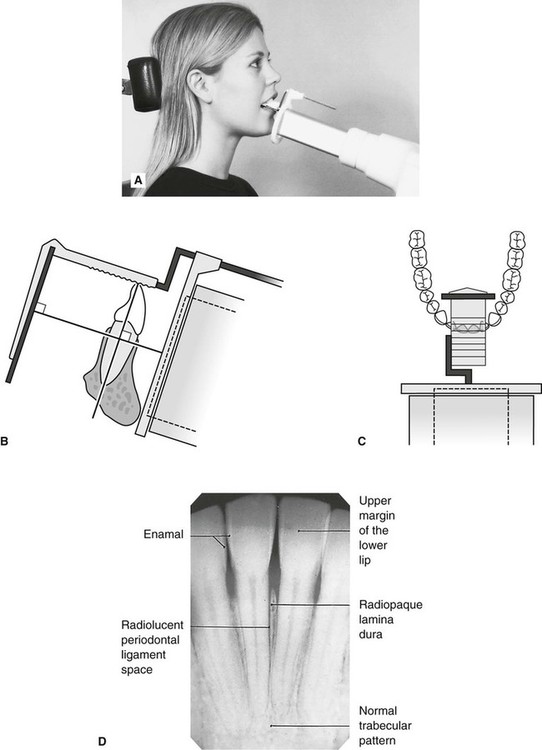
By using a film sensor holder with still. Parallel technique The image receptor is placed in a holder and placed in the mouth parallel to the longitudinal axis of the tooth under.
Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
Basically there are two techniques for taking periapical radiography.
. In these situations the bisecting angle technique may be used. The paralleling technique is recommended for routine periapical radiography but there are some instances when it is very difficult due to patient anatomy or lack of cooperation. Periapical radiography is a commonly used intraoral imaging technique in radiology and may be a component of your radiologic examination.
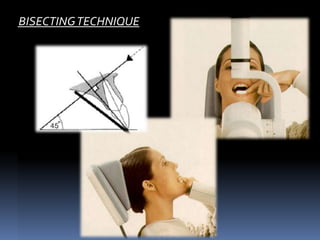
The Bisecting Angle Technique is an alternative to the paralleling technique for taking periapical films. What are periapical radiographs used for. The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays.
Periapical images have been collected using the FONA X70 Intraoral X-rays machine and PSPIX Imaging Plates. The X-ray is taken and the exposed plate is then loaded into a scanner or processor which reads the image. Paralleling Technique for Periapical X-rays The paralleling technique results in good quality x-rays with a minimum of distortion and is the most reliable technique for taking periapical x-rays.
Paralleling technique Bisecting angle technique Paralleling technique It is also called the extension cone paralleling technique right angle technique and long cone technique. Have the more e ectively the m odel works. There are two types of techniques used for periapical radiographs.
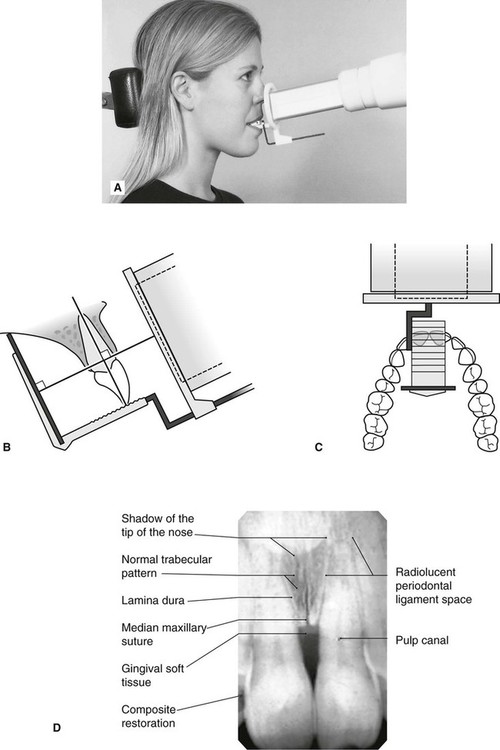
Inclusion criteria included periapical X-ray images of permanents teeth and patients aged 14 years old with good sharpness. Intraoral periapical radiographs can be produced using two different techniques. The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth in question and the central x-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth.
The image receptor is placed in a holder and positioned in the mouth parallel to the long axis of the tooth under. Bisecting angle and paralleling. The bisecting technique may have to be used for patients unable to accommodate the film positioning device used in the paralleling technique.
All radiographs were obtained by digital x. Periapical X-rays show the entire tooth from the exposed crown to the end of the root and the bones that support the tooth. The patient was positioned upright with hisher mouth was opened as wide as possible to allow the X-ray beam to pass to the sensor unobstructed from the opposite side of the mouth.
The Long Cone Paralleling Technique. Ensure they are seated high enough so it is easy to see the occlusal. Periapical X-rays are used to detect any abnormalities of the root structure and surrounding bone structure.
The X-ray tubehead is then aimed at right angles vertically and horizontally to both the tooth and the image. Each X-ray reveals the entire arch of teeth in either the upper or lower jaw. Extraoral radiograph Panoramic X-ray Tomograms Cephalometric projections Sialography Computed tomography 10.
With this technique the film is placed parallel to the long axis of a tooth allowing the X-ray to be focused perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. A long cone is used to take x-rays with paralleling exposure techniques. Periapical radiographs provide important information about the teeth and surrounding bone.
The X-ray head is directed at right angles vertically and horizontally of both the tooth and the image receptor. Periapical film is held parallel to the long axis of the tooth using film-holding instruments. Most frequently used radiography is for the periapical which is performed by the bisecting Thus when considering the execution of the radiographic technique and the possibility of errors that occur during the exposure of X-ray image XR receptors it is important to identify those that occur more frequently.
The extraoral periapical radiographic technique was performed for both maxillary and mandibular teeth using Newman and Friedman technique2. The sensor was placed on the. Exclusion criteria were periapical X-ray images of tooth germs or images which have distortion effects.
Occlusal X-rays show full tooth development and placement 9. Occlusal X-rays are larger and show full tooth development and placement. These X-rays are used to find dental problems below the gum line or in the jaw such as impacted teeth tooth fractures abscesses tumours and bone changes linked to some diseases.
4 Which technique is most often used when exposing a periapical image. To take a periapical exposure the hygienist or x-ray technician places a small photosensitive imaging plate coated with phosphorus into a sterile wrapper and inserts it into the patients mouth just like a conventional X-ray film card. 3 What is an intraoral technique of exposing periapical images.
The central ray is directed to pass at a perpendicular angle to both the tooth and the film. 6 Which exposure technique does the American Academy of Oral and Maxillofacial Radiology and the American Dental Education Association recommend. What are the techniques for periapical radiography.
Since the slope and curvature of the dental arches and the alveolar processes will not permit the film to be held close to the teeth. 5 What is bisecting angle technique in dentistry. Periapical X-rays.
By using a filmsensor holder with fixed image receptor and. The film is placed parallel to the long axis of the tooth in question and the central x-ray beam should be directed perpendicular to the long axis of the tooth. The patient is seated upright in the dental chair and should remove any removable dental appliances glasses or jewelry that could interfere with the X-ray beam.
Periapical X-ray images expor ting results and reading results. 50 patients had their periapical dental radiographs taken utilizing the long cone paralleling technique. Machine learning techniques th e more images in the dataset we.
The bisecting-the-angle technique and the more commonly used long cone paralleling technique. Periapical X-rays are used to detect any abnormalities of the root structure and surrounding bone structure.
Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry
Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate

Periapical Radiography Clinical Gate
Periapical Radiography Pocket Dentistry

0 comments
Post a Comment